





Heating Method: “Induction heating systems are used. Induction heating provides faster and more controlled heating,” making the material ready for the forging process
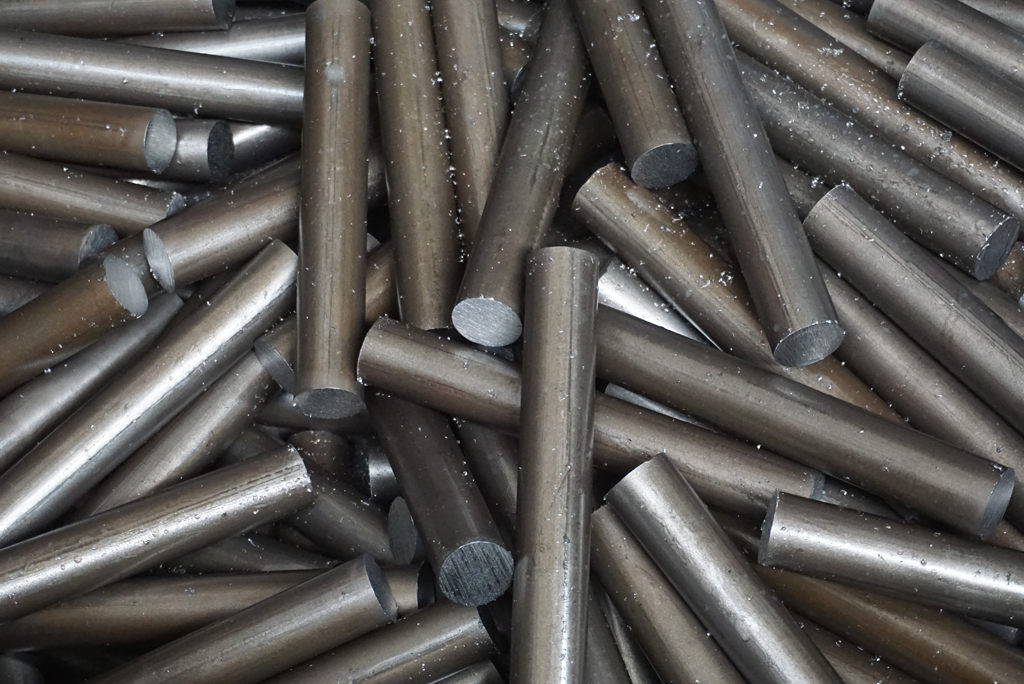


The head of the bolt is another critical part shaped during the forging process. This head is usually round, hexagonal, or square. The shaping process often involves forging, and commonly used head shapes include hexagonal and cap-style expanding designs. The head is typically formed with the aid of a mold.
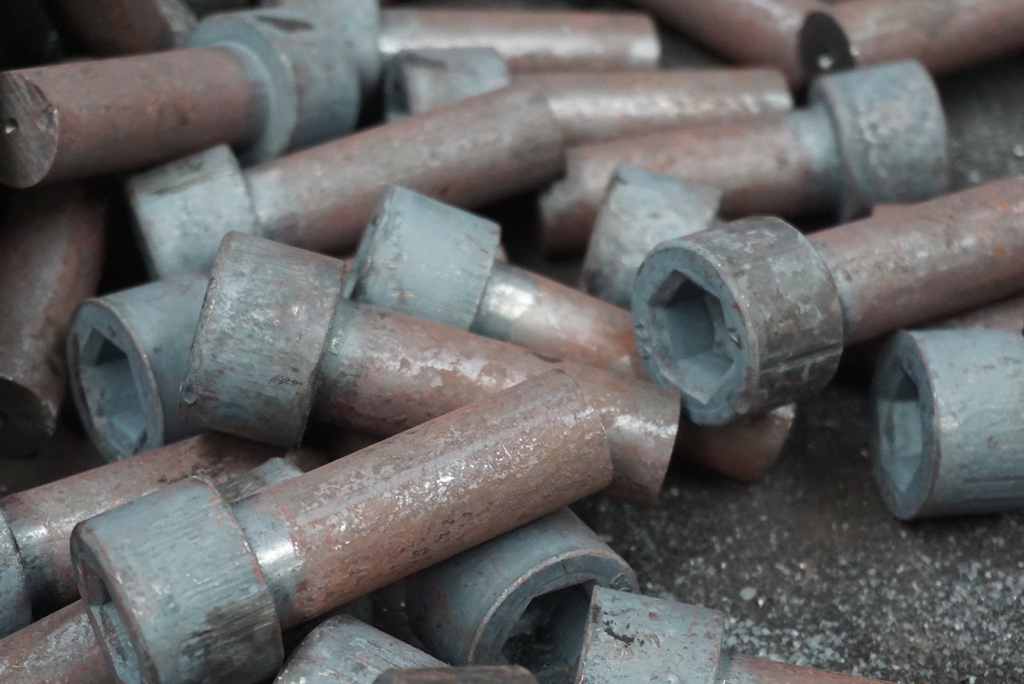

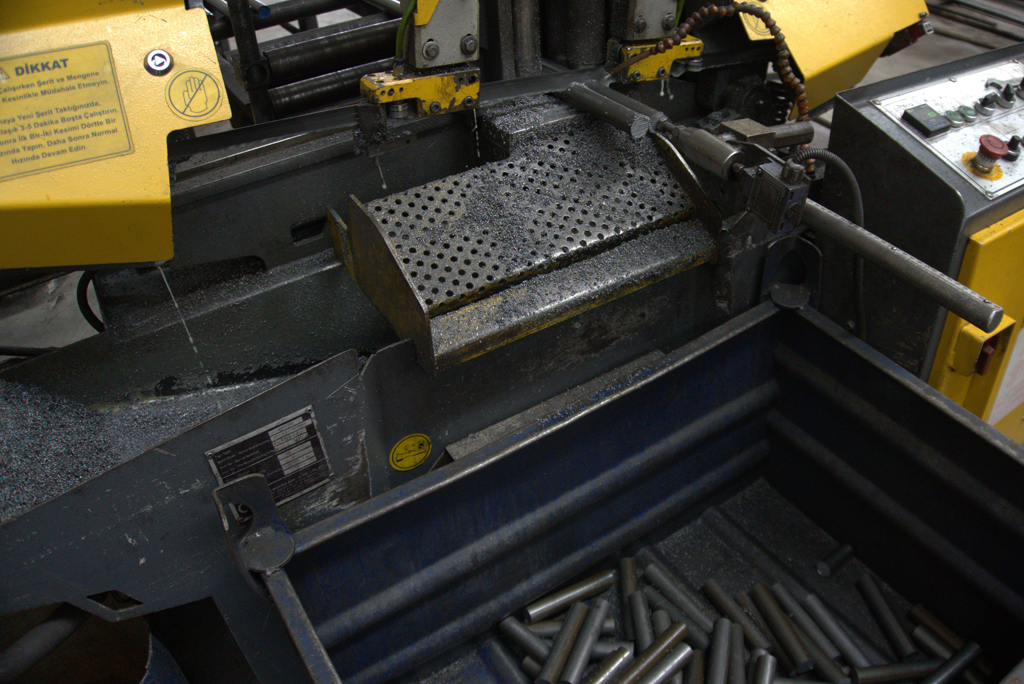
– The machining phase of bolt production involves the final processing steps. This stage is especially critical for precisely forming the bolt’s thread structure.
Thread Rolling: The threads of the bolt are typically formed through a process called “thread rolling.” In this process, no material is cut; instead, the shape of the metal is altered, resulting in threads that are stronger and more durable.

The threads of the bolt are typically formed through a process called “thread rolling.” In this process, no material is cut; instead, the shape of the metal is altered, resulting in threads that are stronger and more durable.
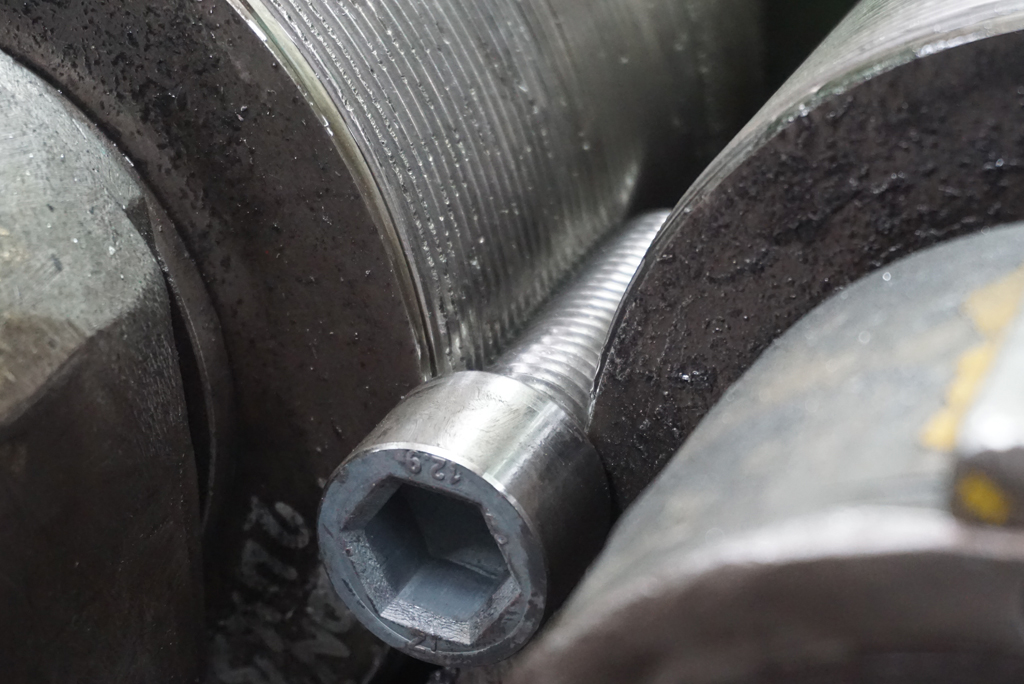

To enhance the durability of bolts, surface coating processes such as galvanizing, nitriding, chrome plating, zinc plating, or Geomet coating can be applied. These treatments make the bolts more resistant.
Sizing, Testing, and Packaging:
The final stage of bolt production is quality control testing. This step includes tests to verify the bolt’s durability, dimensions, and overall functionality. The completed bolts are packaged and prepared for distribution, ensuring delivery within the specified time frame.

You can contact us for your production requests.